¶ What is Air Printing Detection
During 3D printing, "air printing" occurs when the nozzle fails to extrude filament properly due to clogs, damp/irregular filament, or incorrect temperature settings, causing the nozzle to print in mid-air. The H2 series printer uses multi-module collaboration to detect air printing, pausing immediately and prompting users to resolve the issue. It should be noted that the H2S does not support nozzle-camera vision detection for air printing.

¶ Three Detection Solutions
¶ **1. Camera-Based Visual Detection (Monitors Nozzle Extrusion) **
Since it does not have a nozzle camera, the H2S does not support vision-based air printing detection.
¶ How It Works
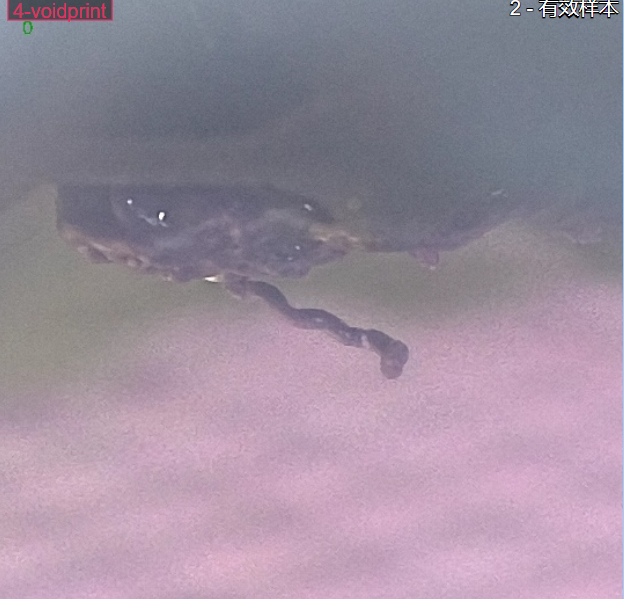
The nozzle camera continuously checks two critical conditions:
-
No filament is extruded when expected.
-
The distance between the nozzle and the printed object increases over time.

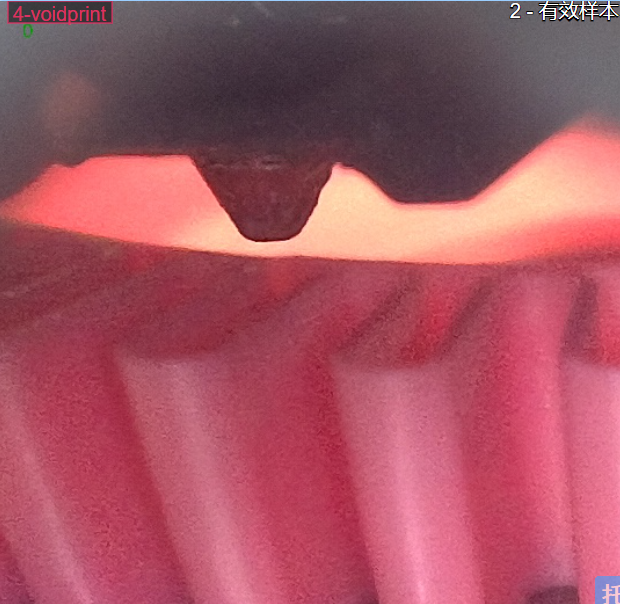 |
 |
¶ Requirements
- The printer must be equipped with a nozzle camera.
¶ Conditions for Use
-
The nozzle camera and auxiliary fill light must function properly, with a clean lens.
-
Enable the "AI Print Monitoring" option in print settings.
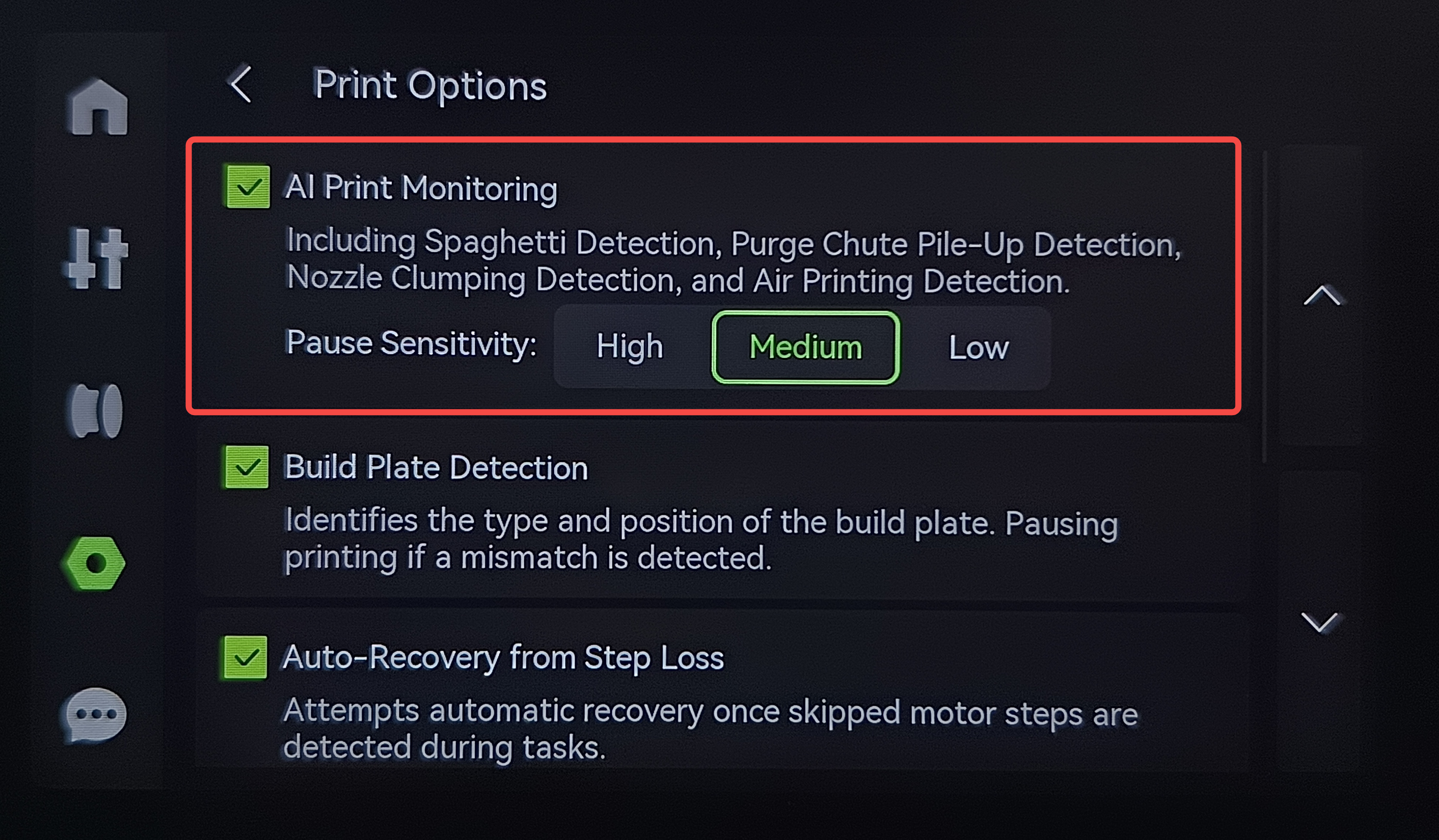
¶ Notes
False Alerts: Models with long traveling (e.g., scattered small parts) may trigger false alarm.
Accuracy: Due to limited training data in the current firmware version, detection accuracy is being continuously improved through algorithm updates.
¶ 2. AMS-Based Detection (Measures Filament Feed Length)
¶ How It Works
The AMS continuously monitors the filament feed length during printing:
- If feeding length remains unchanged → Extrusion failure is detected → Filament is automatically cut and retracted.
¶ Requirements
- Enabled by default when using AMS for printing.
¶ Notes
Error Handling:
When an air printing error occurs, the printer automatically cuts the filament and pulls it back to the AMS. To resolve:
-
Pull the filament from the corresponding AMS slot.
-
Trim damaged sections (e.g., worn filament).
-
Reinsert the filament and resume printing.
-
If extrusion errors persist, check for nozzle clogs or extruder jams.
Post-Recovery Check:
- Under-extrusion may appear on the model surface due to air printing that occurred before detection. Inspect the print quality before deciding to continue or restart the task.
¶ 3. Closed-Loop Servo Motor Detection (Senses Extrusion Resistance)
¶ How It Works
Monitors the servo motor’s torque output:
- High extrusion speed + low torque → Indicates gear slippage (e.g., filament not grabbed or worn down).
The H2D uses a closed-loop servo motor to track torque in real time. If rapid extrusion speed is paired with abnormally low torque, the system detects extrusion failure.
¶ Common causes include:
-
Manually loaded external filament triggering the hall sensor but not being grabbed by gears.
-
Filament wear reduces its diameter, preventing proper grip.
¶ Requirements
- Enabled by default when using external spools.
¶ Conditions for Use
-
External spool printing only
-
0.4mm nozzle required (other sizes unsupported)
-
The print speed must be moderate: Detection requires a print flow rate >9.6 mm³/s (low-speed scenarios like first-layer printing may bypass detection)
-
Supported materials: PLA, PLA-CF, PETG, PETG-CF
¶ Troubleshooting Steps:
-
Trim damaged sections of filament.
-
Reinsert filament → Preheat nozzle → Manually test extrusion.
-
If extrusion fails, check and clear the nozzle/clogged extruder.
¶ Notes:
- Less effective for models with frequent retractions (e.g., tall thin pillars).
- Post-recovery prints may show minor material gaps due to delayed alerts (affected by material type/speed). Inspect print quality carefully before deciding to resume the print.
¶ Application Scenarios
In summary, the system automatically activates dual detection based on the material feeding method:
When Using AMS:
-
Camera Detection: Monitors nozzle extrusion status. (Not including H2S)
-
AMS Feed Tracking: Precisely measures filament feeding length.
When Using External Spools:
-
Camera Detection: Monitors nozzle extrusion status. (Not including H2S)
-
Motor Torque Detection: Tracks extrusion resistance changes.
By combining two detection methods, the H2 series ensures higher sensitivity to air printing in both scenarios, significantly improving print reliability and success rates.
¶ End Notes
We hope the detailed guide provided has been helpful and informative.
If this guide does not solve your problem, please submit a technical ticket, we will answer your questions and provide assistance.
If you have any suggestions or feedback on this Wiki, please leave a message in the comment area. Thank you for your support and attention!