¶ H2D
¶ Front View
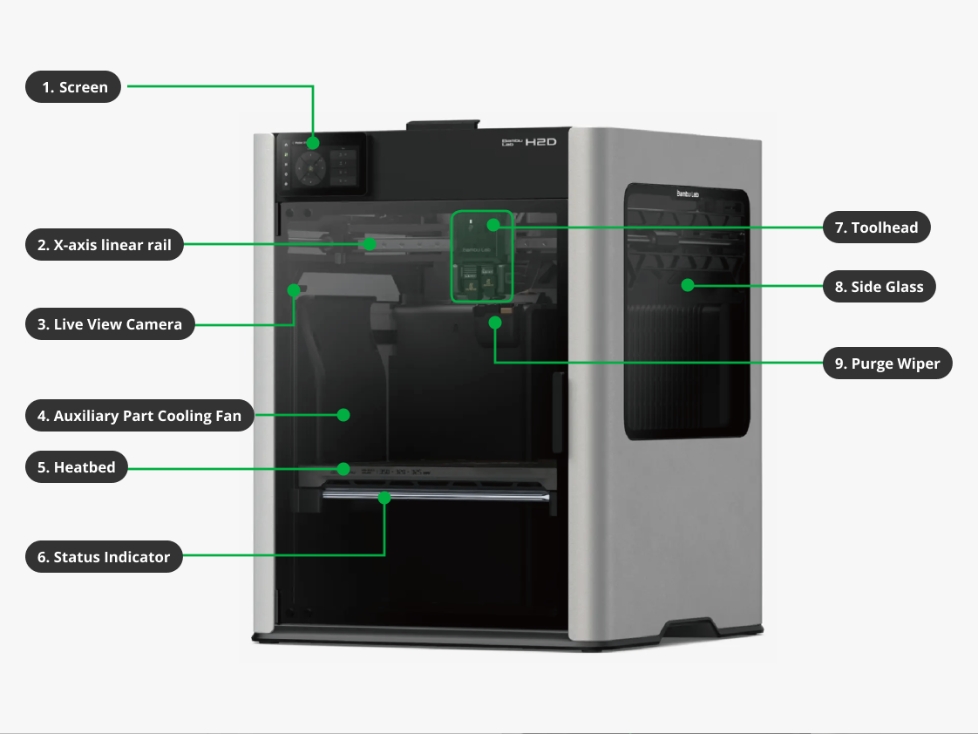
| 1. Screen | Displays printing parameters and controls the printer. |
| 2. X-Axis Linear rail | Ensures that the toolhead maintains a stable and precise position on the X-Axis (left and right movement). |
| 3. Live View Camera | Records and transmits images of the printing process for live monitoring or automatic compilation into timelapse videos of the full printing process. It is also used as a video data source for AI error detection functionality. |
| 4. Auxiliary Part Cooling Fan | A powerful cooling fan installed on the left side of the chamber. It provides cooling air circulation which improves conditions for high-speed printing. |
| 5. Heatbed | The support platform for the build plate where the 3D model is attached and printed. Aside from providing the stable platform with precise movement on the Z-Axis controlling the height of printing, also heats the build plate to provide ideal adhesion properties depending on printing materials. |
| 6. Status Indicator | An LED light bar which displays different patterns and colors to communicate the status of the printer as it relates to printing progress, printing errors, and more. |
| 7. Toolhead | The apparatus which provides solid mounting for printing hardware such as the extruder, hotends, and circuit boards which connect this hardware. In the case of the H2D, contains 2 separate hotends, nozzles, and filament inputs as well as a mechanism to switch the extruder between the left and right hotend. Moves on the XY plane at the top of the print enclosure. |
| 8. Side Glass | Viewing windows on either side of the H2D enclosure which allow the workpiece or hardware within the enclosure to be viewed from side-on. In the case of the Laser equipped H2D, this glass has a green laser safety tint installed. |
| 9. Purge Wiper | A set of nozzle cleaning tools which detach unwanted filament purge or print debris from the nozzles to prevent contamination of the 3D part. |
¶ Toolhead View
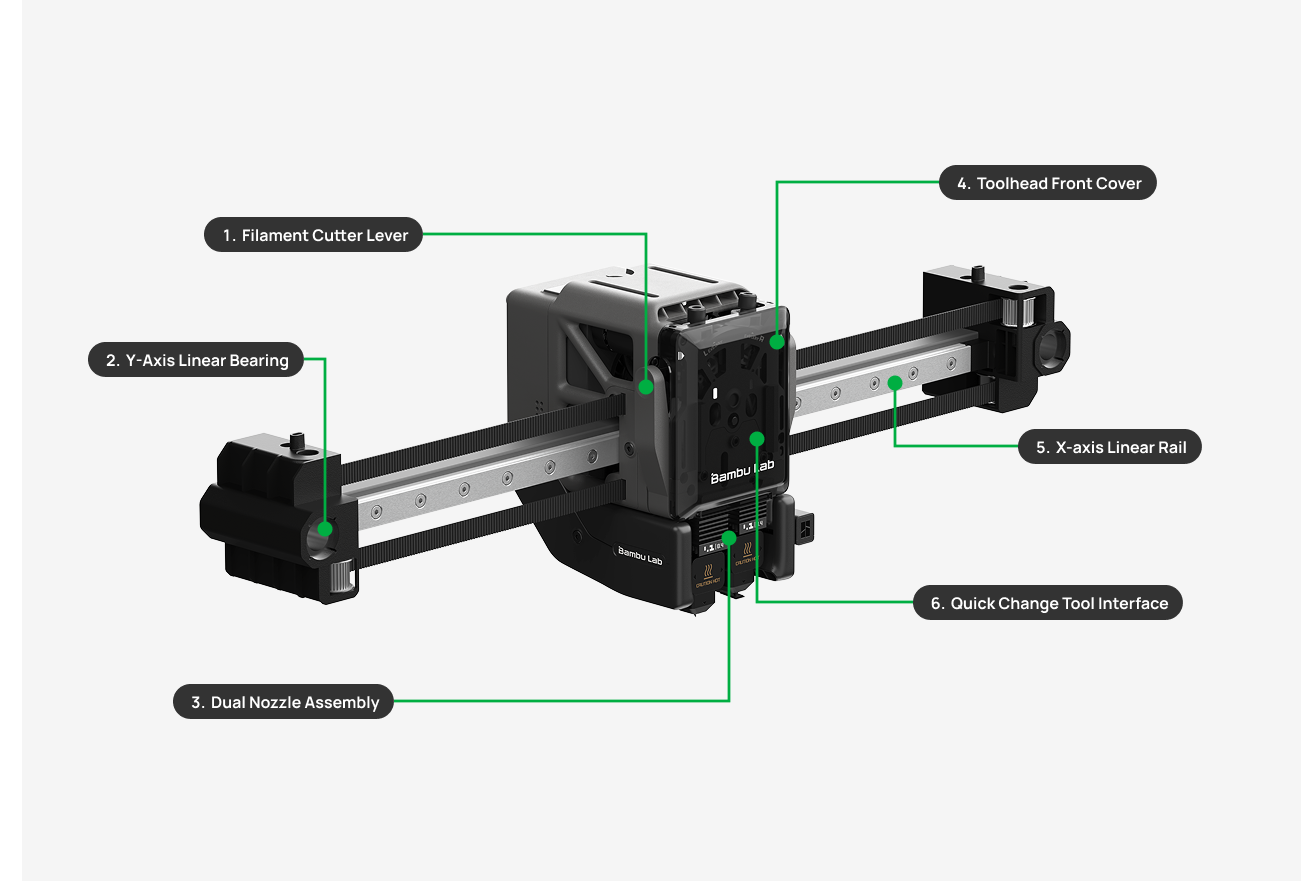
| 1. Filament Cutter Lever | Used for holding the cutter and pushing it to cut filaments. |
| 2. Y-axis | Ensures that the toolhead maintains a stable and precise position on the Y-Axis (forward and backward movement). |
| 3. Dual Nozzle Assembly | Holds the two hotends/nozzles and switches between them by moving the left hotend up and down. |
| 4. Toolhead Front Cover | Designed to protect the front part of the toolhead. Covers and protects the Quick Change Tool interface and keeps debris from the extruder gears and internal mechanisms. |
| 5. X-axis Linear Rail | Ensures that the toolhead maintains a stable and precise position on the X-Axis (left and right movement). |
| 6. Quick Change Tool Interface | Links the FPC cable and indicator lights for both extruders while offering a seamless attachment point for the laser and cutting modules. |
¶ H2S
¶ Front View
.png)
| 1. Screen | Displays printing parameters and controls the printer. |
| 2. X-axis Linear rail | Ensures the toolhead remains fixed on a horizontal surface during X-axis movement. Its lightweight and high rigidity enable stable and fast movement of the toolhead along the X-axis, enabling high-speed printing. |
| 3. Live View Camera | The H2S Live View Camera has a 1920×1080 resolution at 30fps. It allows users to monitor the printer chamber in real time, capture time-lapse videos, and supports AI detection functions for smarter printing management. |
| 4. Auxiliary Part Cooling Fan | A powerful cooling fan installed on the left side of the chamber. It generates airflow over the currently printed layer, which improves conditions for high-speed printing. |
| 5. Toolhead | The main assembly which contains the extruder, filament inlet, hotend, toolhead camera and other electronics. |
| 6. Purge Wiper | The purge wiper is the unit used to clean the nozzle. During printing, the nozzle first passes over a coarse wiping strip to remove larger filament residues. It then moves over a silicone strip for fine cleaning, ensuring the nozzle tip is fully clean and ready for precise printing. |
| 7. Heatbed | The primary function of the heatbed is to heat the printing surface, helping the printed layers adhere better to the build plate. Without heat, the deposited filament cools rapidly, and the tension between the layers can cause warping. |
| 8. Status Indicator | An LED light bar which displays different patterns and colors to communicate the status of the printer as it relates to printing progress, printing errors, and more. |
¶ Toolhead View
.png)
| 1. X-axis Linear Rail | This fan ensures the toolhead remains horizontal during X-axis movement. Its lightweight and high rigidity enable stable and fast X-axis movement, enabling high-speed printing. |
| 2. Cooling Fan for Hotend | Its main role is to keep the hotend temperature stable, preventing overheating and reducing the risk of nozzle clogging. |
| 3. Part Cooling Fan | The part cooling fan channels air through a duct, directing it precisely around the nozzle. This focused airflow quickly cools the freshly extruded filament, enhancing layer bonding, minimizing warping, and ensuring consistent print quality. |
| 4. X Belt | The X Belt is a key transmission component on the X-axis. The belt links the X motor to the toolhead, ensuring smooth and precise movement. |
| 5. Toolhead Camera | A 1600×1200 resolution camera at 30fps is built into the toolhead for motion accuracy calibration, ensuring precise printing. |
| 6. Silicone Sock for Hotend | It provides optimal thermal insulation for the hotend, allowing it to maintain a stable temperature during printing, while also providing durable protection to prevent filament from sticking to the hotend. |
¶ X1 Series
¶ Front View
.png)
| 1. Screen | Displays printing parameters and controls the printer. |
| 2. LED Light | It is a lighting device mounted on the 3D printer, used to provide additional illumination so that users can clearly observe the printing process. |
| 3. XY Belt | It is an open drive belt with a pitch length of 1442mm for X1 and P1 series printers. Its main function is to transmit the motion of the motor to the tool head with high precision. |
| 4. Live view camera | Records and transmits images of the printing process for live monitoring or automatic compilation into timelapse videos of the full printing process. It is also used as a video data source for AI error detection functionality. |
| 5. Auxiliary Part Cooling Fan | A powerful cooling fan installed on the left side of the chamber. It provides cooling air circulation which improves conditions for high-speed printing. |
| 6. Z-axis Threaded Rod | It is used to control the vertical movement of the heatbed. |
| 7. Micro SD | It is used to store files such as print files, cached files, and videos of the printing process. |
| 8. Toolhead | It contains multiple parts like the extruder, hotend and toolhead board. |
| 9. X-axis Carbon Rods Assembly | It ensures that the X-axis movement of the toolhead remains consistently fixed on the horizontal plane. Its lightweight and high rigidity characteristics enable the toolhead to achieve stable and high-speed movement along the X-axis, enabling high-speed printing. |
| 10. Purge Chute | It is installed on the back of the printer and used to slide the excess filament out of the printer. |
| 11. Heatbed | The support platform for the build plate where the 3D model is attached and printed. Aside from providing the stable platform with precise movement on the Z-Axis controlling the height of printing, also heats the build plate to provide ideal adhesion properties depending on printing materials. |
| 12. Bambu Textured PEI Plate | It is made by coating a stainless steel sheet with a layer of PEI powder, creating a textured surface on both sides. What sets it apart is its special rough texture, which is transferred to the bottom surface of your prints. This plate works well with a variety of materials and often provides excellent adhesion without the need for adhesives, making it user-friendly. Additionally, the PEI coating on the plates is durable and has a long lifespan. |
¶ Toolhead View
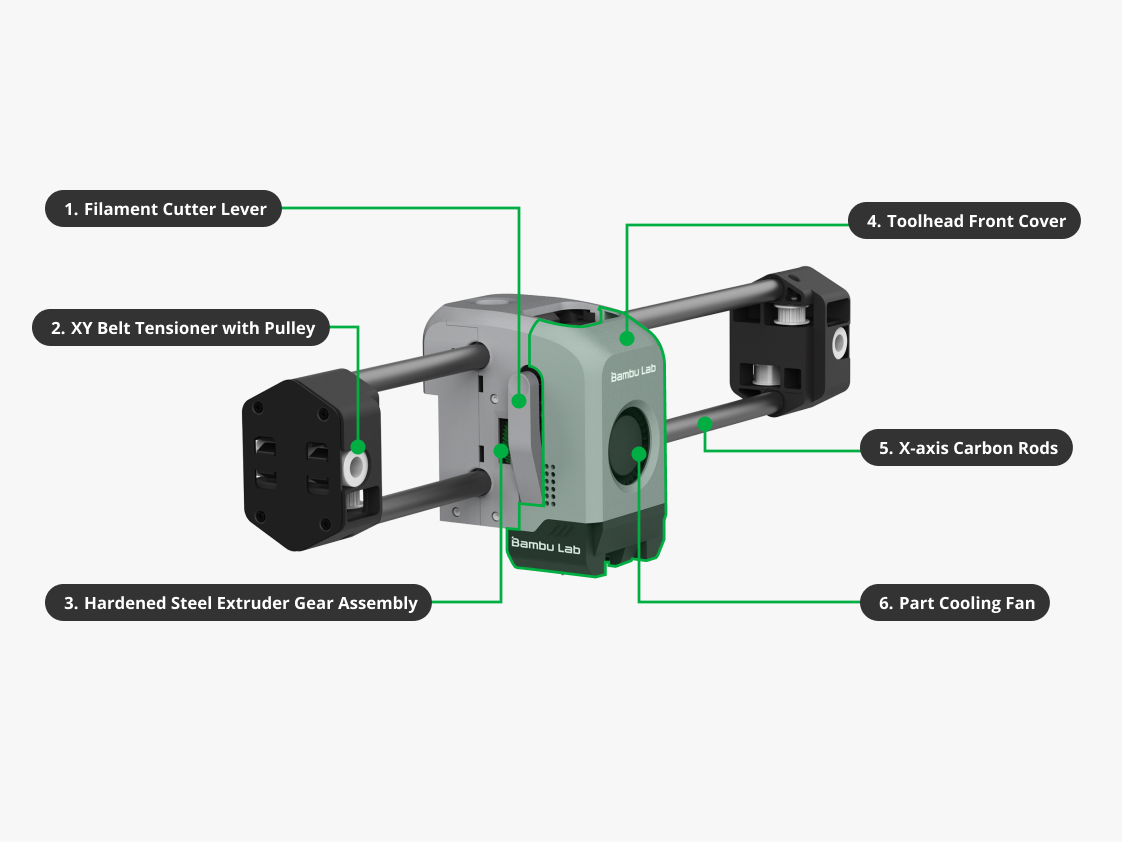
| 1. Filament Cutter Lever | It is used for holding the cutter and pushing it to cut filaments. |
| 2. XY Belt Tensioner with Pulley | It is composed of an idler pulley and a bracket, which can change the belt travel distance under the tension of the spring. |
| 3. Hardened Steel Extruder Gear Assembly | It is an internal gear component of the extruder unit. It comprises a driven gear and an active gear that work together to feed filament into the hotend. |
| 4. Toolhead Front Cover | It is designed to protect the front part of the toolhead. For A1 series printer, it features a circular window that allows observation of the rotating status of the extruder gear; for X1/P1 series printers, it also contains the part cooling fan. |
| 5. X-axis Carbon Rods | It ensures that the X-axis movement of the toolhead remains consistently fixed on the horizontal plane. Its lightweight and high rigidity characteristics enable the toolhead to achieve stable and high-speed movement along the X-axis, enabling high-speed printing. |
| 6. Part Cooling Fan | It is used to ensure adequate cooling of the printed layers during the printing process. It helps in rapidly cooling the material as it is extruded, allowing each layer to solidify and maintain its shape before the next layer is deposited. |
¶ P1 Series
¶ Front View
.jpg)
| 1. Screen | Displays printing parameters and controls the printer. |
| 2. LED Light | It is a lighting device mounted on the 3D printer, used to provide additional illumination so that users can clearly observe the printing process. |
| 3. XY Belt | It is an open drive belt with a pitch length of 1442mm for X1 and P1 series printers. Its main function is to transmit the motion of the motor to the tool head with high precision. |
| 4. Live view camera | Records and transmits images of the printing process for live monitoring or automatic compilation into timelapse videos of the full printing process. |
| 5. Auxiliary Part Cooling Fan | A powerful cooling fan installed on the left side of the chamber. It provides cooling air circulation which improves conditions for high-speed printing. |
| 6. Z-axis Threaded Rod | It is used to control the vertical movement of the heatbed. |
| 7. Micro SD | It is used to store files such as print files, cached files, and videos of the printing process. |
| 8. Toolhead | It contains multiple parts like the extruder, hotend and toolhead board. |
| 9. X-axis Carbon Rods Assembly | It ensures that the X-axis movement of the toolhead remains consistently fixed on the horizontal plane. Its lightweight and high rigidity characteristics enable the toolhead to achieve stable and high-speed movement along the X-axis, enabling high-speed printing. |
| 10. Purge Chute | It is installed on the back of the printer and used to slide the excess filament out of the printer. |
| 11. Heatbed | The support platform for the build plate where the 3D model is attached and printed. Aside from providing the stable platform with precise movement on the Z-Axis controlling the height of printing, also heats the build plate to provide ideal adhesion properties depending on printing materials. |
| 12. Bambu Textured PEI Plate | It is made by coating a stainless steel sheet with a layer of PEI powder, creating a textured surface on both sides. What sets it apart is its special rough texture, which is transferred to the bottom surface of your prints. This plate works well with a variety of materials and often provides excellent adhesion without the need for adhesives, making it user-friendly. Additionally, the PEI coating on the plates is durable and has a long lifespan. |
¶ Toolhead View

| 1. Filament Cutter Lever | It is used for holding the cutter and pushing it to cut filaments. |
| 2. XY Belt Tensioner with Pulley | It is composed of an idler pulley and a bracket, which can change the belt travel distance under the tension of the spring. |
| 3. Hardened Steel Extruder Gear Assembly | It is an internal gear component of the extruder unit. It comprises a driven gear and an active gear that work together to feed filament into the hotend. |
| 4. Toolhead Front Cover | It is designed to protect the front part of the toolhead. For A1 series printer, it features a circular window that allows observation of the rotating status of the extruder gear; for X1/P1 series printers, it also contains the part cooling fan. |
| 5. X-axis Carbon Rods | It ensures that the X-axis movement of the toolhead remains consistently fixed on the horizontal plane. Its lightweight and high rigidity characteristics enable the toolhead to achieve stable and high-speed movement along the X-axis, enabling high-speed printing. |
| 6. Part Cooling Fan | It is used to ensure adequate cooling of the printed layers during the printing process. It helps in rapidly cooling the material as it is extruded, allowing each layer to solidify and maintain its shape before the next layer is deposited. |
¶ A1
¶ Front View
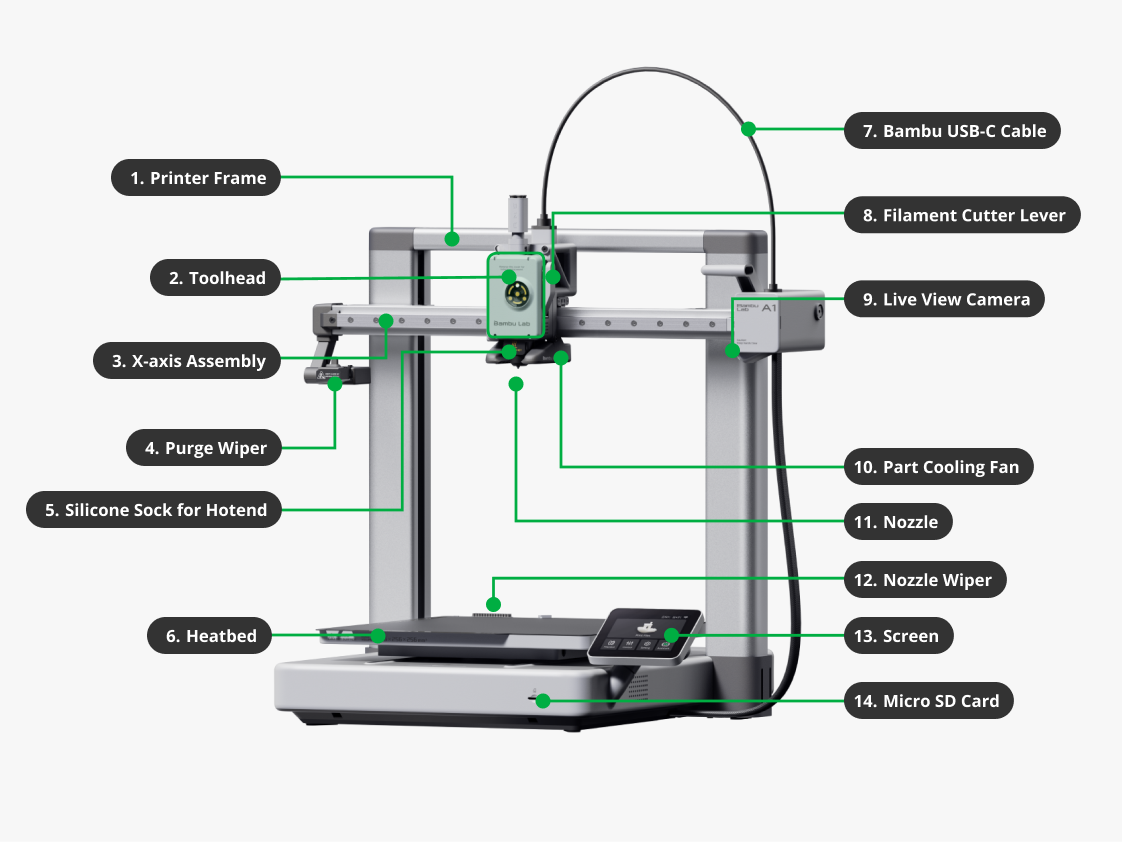
| 1. Printer Frame | It is the structural framework of the A1 series printers that supports the printhead and heatbed, ensuring stability during the printing process. |
| 2. Toolhead | It contains multiple parts like the extruder, hotend and toolhead board. |
| 3. X-axis Assembly | It ensures that the X-axis movement of the toolhead remains consistently fixed on the horizontal plane. The X-axis utilizes linear rail guidance, which provides stability, smooth motion, improved guiding precision, and longevity. |
| 4. Purge Wiper | It is designed to efficiently remove waste filament generated by the printer's hotend. It gathers and dislodges waste filament during different stages, including printer setup, pause and resume operations, and filament changes for multi-color printing. Its purpose is to ensure the proper management and disposal of waste materials for seamless printing processes. |
| 5. Silicone Sock for Hotend | It is made from high-quality silicone for higher temperature resistance (rated to 300°C). It provides optimal thermal insulation for the hotend to maintain a consistent temperature during printing, while also offering long-lasting protection from filament being stuck to the hotend. |
| 6. Heatbed | The support platform for the build plate where the 3D model is attached and printed. Aside from providing the stable platform with precise movement on the Y-Axis controlling forward and backward movement relative to the toolhead, also heats the build plate to provide ideal adhesion properties depending on printing materials. |
| 7. Bambu USB-C Cable | Used for communication between the toolhead and the mainboard. |
| 8. Filament Cutter Lever | It is used for holding the cutter and pushing it to cut filaments. |
| 9. Live view camera | The camera has two functions: remote live streams and timelapse. The X1, P1 and A1 series printers are equipped with a camera by default. |
| 10. Part Cooling Fan | It is used to ensure adequate cooling of the printed layers during the printing process. It helps in rapidly cooling the material as it is extruded, allowing each layer to solidify and maintain its shape before the next layer is deposited. |
| 11. Nozzle | With a integrated design, the nozzle is integrated into the heater and connected to the heat sink via a thin metal tube for optimal performance. This design allows the hotend to heat up much faster than a normal hotend, and also effectively minimizes problems that can occur when changing nozzles. In contrast to stainless steel nozzles, hardened steel nozzles can print carbon or glass fiber reinforced or particle filled materials such as PLA-CF/GF, PETG-CF/GF, ABS-CF/GF, PA-CF/GF, PAHT-CF/GF, PET-CF/GF, PLA-Marble and PLA Sparkle. |
| 12. Nozzle Wiper | It is a flexible tool mounted on the edge of the purge chute and is used to clean the waste overflowing from the printer nozzle before printing. |
| 13. Screen | Displays printing parameters and controls the printer. |
| 14. Micro SD Card | It is used to store files such as print files, cached files, and videos of the printing process. |
¶ Side View
.png)
| 1. X-axis Motor | It is utilized to drive the toolhead left and right along the X-axis. |
| 2. TH Board | It is responsible for processing printing commands and controlling the device's functions. |
| 3. Y Belt | It is a crucial transmission component within the Y-axis assembly, facilitating the connection between the Y motor and the heatbed, enabling smooth movement along the Y-direction. It is imperative to replace the Y-axis belt promptly in cases of severe wear or breakage to avoid disrupting printer operations. |
| 4. Z-axis Motor | It is a stepper motor that drives the movement of the heatbed in the Z-axis direction through the Z-axis synchronous belt. A motor cable and a driving wheel are included. |
| 5. Z-axis Top Cover | It is designed to protect the top of the Z-axis assembly. |
| 6. X Belt | It is a crucial transmission component within the X-axis assembly, facilitating the connection between the X motor and the tool head, enabling smooth movement along the X-direction. It is imperative to replace the X belt promptly in cases of severe wear or breakage to avoid operational disruptions of the printer. |
| 7. Y-axis Top Cover | It is the protective cover over the top of the Y-axis assembly, preventing dust and debris from entering. |
| 8. Z Belt | Its main function is to transmit the motion of the Z motor to the three Z-axis lead screws. |
¶ Toolhead View
.png)
| 1. Extruder Filament Sensor | It is installed on the extruder to detect whether the current printing filament has been delivered to the extruder and whether the cutter rod is released normally. |
| 2. Extruder Unit | It is responsible for pulling the filament out of the spool and feeding it into the hotend. The extruder needs to accurately control the length of the filament extruded through the hotend and is one of the core components of a 3D printer. |
| 3. Cooling Fan for Hotend | It is used to enhance the temperature conduction of the hotend hea sink and prevent heat from being conducted to other components such as the extruder. The cooling fan is a high-speed rotating part, so do not touch it while it is running. |
| 4. Hotend with nozzle | With a integrated design, the nozzle is integrated into the heater and connected to the heat sink via a thin metal tube for optimal performance. This design allows the hotend to heat up much faster than a normal hotend, and also effectively minimizes problems that can occur when changing nozzles. In contrast to stainless steel nozzles, hardened steel nozzles can print carbon or glass fiber reinforced or particle filled materials such as PLA-CF/GF, PETG-CF/GF, ABS-CF/GF, PA-CF/GF, PAHT-CF/GF, PET-CF/GF, PLA-Marble and PLA Sparkle. |
| 5. Bambu USB-C Cable | Used for communication between the toolhead and the mainboard. |
| 6. Toolhead Block | It is used to move the toolhead, ensuring stable movement during the printing process. |
| 7. Extruder Motor | It is installed on the toolhead and used to drive the movement of the extruder. |
| 8. Hotend Heating Assembly | It is used to heat the nozzle to the required temperature. |
| 9. Part Cooling Fan | It is used to ensure adequate cooling of the printed layers during the printing process. It helps in rapidly cooling the material as it is extruded, allowing each layer to solidify and maintain its shape before the next layer is deposited. |
¶ A1 mini
¶ Front View
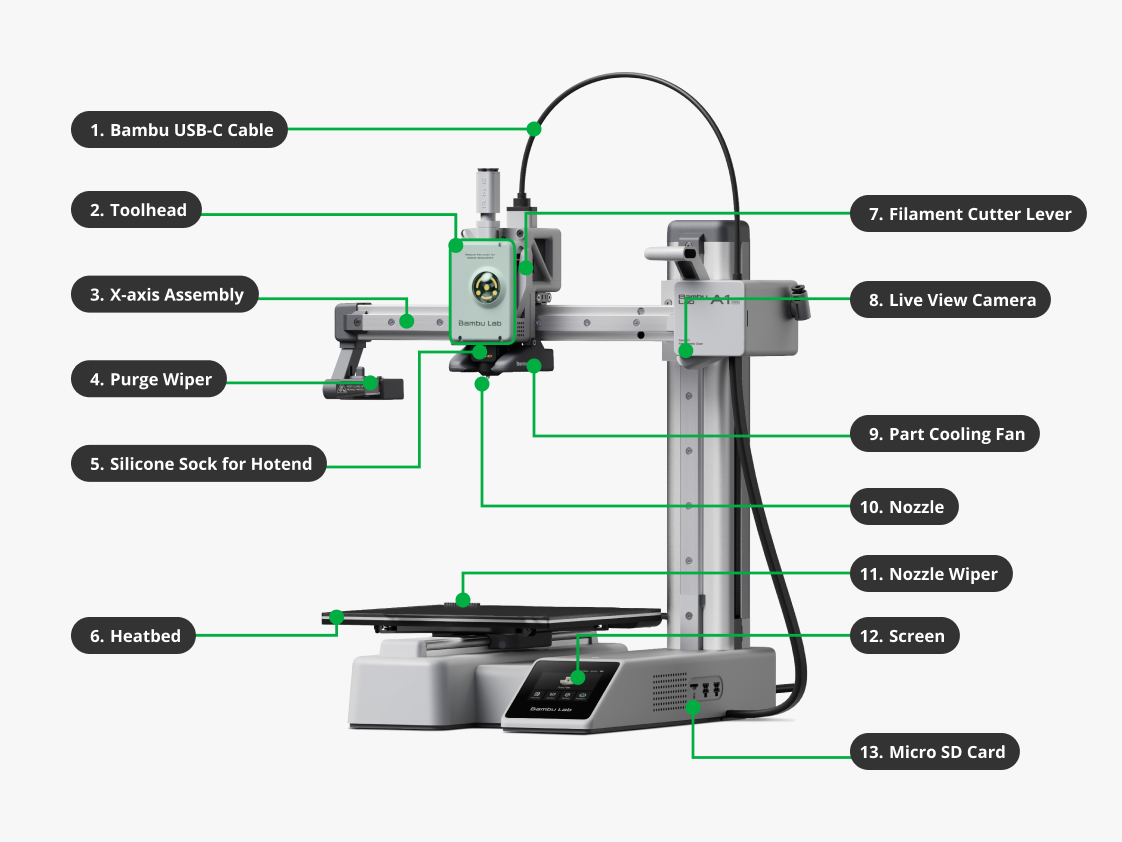
| 1. Bambu USB-C Cable | Used for communication between the toolhead and the mainboard. |
| 2. Toolhead | It contains multiple parts like the extruder, hotend and toolhead board. |
| 3. X-axis Assembly | It ensures that the X-axis movement of the toolhead remains consistently fixed on the horizontal plane. The X-axis utilizes linear rail guidance, which provides stability, smooth motion, improved guiding precision, and longevity. |
| 4. Purge Wiper | It is designed to efficiently remove waste filament generated by the printer's hotend. It gathers and dislodges waste filament during different stages, including printer setup, pause and resume operations, and filament changes for multi-color printing. Its purpose is to ensure the proper management and disposal of waste materials for seamless printing processes. |
| 5. Silicone Sock for Hotend | It is made from high-quality silicone for higher temperature resistance (rated to 300°C). It provides optimal thermal insulation for the hotend to maintain a consistent temperature during printing, while also offering long-lasting protection from filament being stuck to the hotend. |
| 6. Heatbed | The support platform for the build plate where the 3D model is attached and printed. Aside from providing the stable platform with precise movement on the Y-Axis controlling forward and backward movement relative to the toolhead, also heats the build plate to provide ideal adhesion properties depending on printing materials. |
| 7. Filament Cutter Lever | It is used for holding the cutter and pushing it to cut filaments. |
| 8. Live view camera | The camera has two functions: remote live streams and timelapse. The X1, P1 and A1 series printers are equipped with a camera by default. |
| 9. Part Cooling Fan | It is used to ensure adequate cooling of the printed layers during the printing process. It helps in rapidly cooling the material as it is extruded, allowing each layer to solidify and maintain its shape before the next layer is deposited. |
| 10. Nozzle | With a integrated design, the nozzle is integrated into the heater and connected to the heat sink via a thin metal tube for optimal performance. This design allows the hotend to heat up much faster than a normal hotend, and also effectively minimizes problems that can occur when changing nozzles. In contrast to stainless steel nozzles, hardened steel nozzles can print carbon or glass fiber reinforced or particle filled materials such as PLA-CF/GF, PETG-CF/GF, ABS-CF/GF, PA-CF/GF, PAHT-CF/GF, PET-CF/GF, PLA-Marble and PLA Sparkle. |
| 11. Nozzle Wiper | It is a flexible tool mounted on the edge of the purge chute and is used to clean the waste overflowing from the printer nozzle before printing. |
| 12. Screen | Displays printing parameters and controls the printer. |
| 13. Micro SD Card | It is used to store files such as print files, cached files, and videos of the printing process. |
¶ Side View
.png)
| 1. X-axis Motor | It is utilized to drive the toolhead left and right along the X-axis. |
| 2. Z-axis Top Cover | It is designed to protect the top of the Z-axis assembly. |
| 3. TH Board | It is responsible for processing printing commands and controlling the device's functions. |
| 4. Spool Holder Bracket | It is used to mount the filament to the printer when the AMS Lite is not used. |
| 5. Heatbed Cable | It connects the A1 mini heatbed to the mainboard, which is used to power the heatbed and provide feedback on the temperature of the heatbed. |
| 6. X-axis Motor Cover | It is a white closed box used to cover the X motor, including a front cover, a back cover and a middle frame. |
| 7. Extruder Motor | It is installed on the toolhead and used to drive the movement of the extruder. |
| 8. X Belt | It is a crucial transmission component within the X-axis assembly, facilitating the connection between the X motor and the tool head, enabling smooth movement along the X-direction. It is imperative to replace the X Belt promptly in cases of severe wear or breakage to avoid operational disruptions of the printer. |
| 9. Y-axis Motor | It is used to drive the heatbed in the back-and-forth motion along the Y-axis. |
| 10. Y Belt | It is a crucial transmission component within the Y-axis assembly, facilitating the connection between the Y motor and the heatbed, enabling smooth movement along the Y-direction. It is imperative to replace the Y-axis belt promptly in cases of severe wear or breakage to avoid disrupting printer operations. |
¶ AMS
¶ Front View
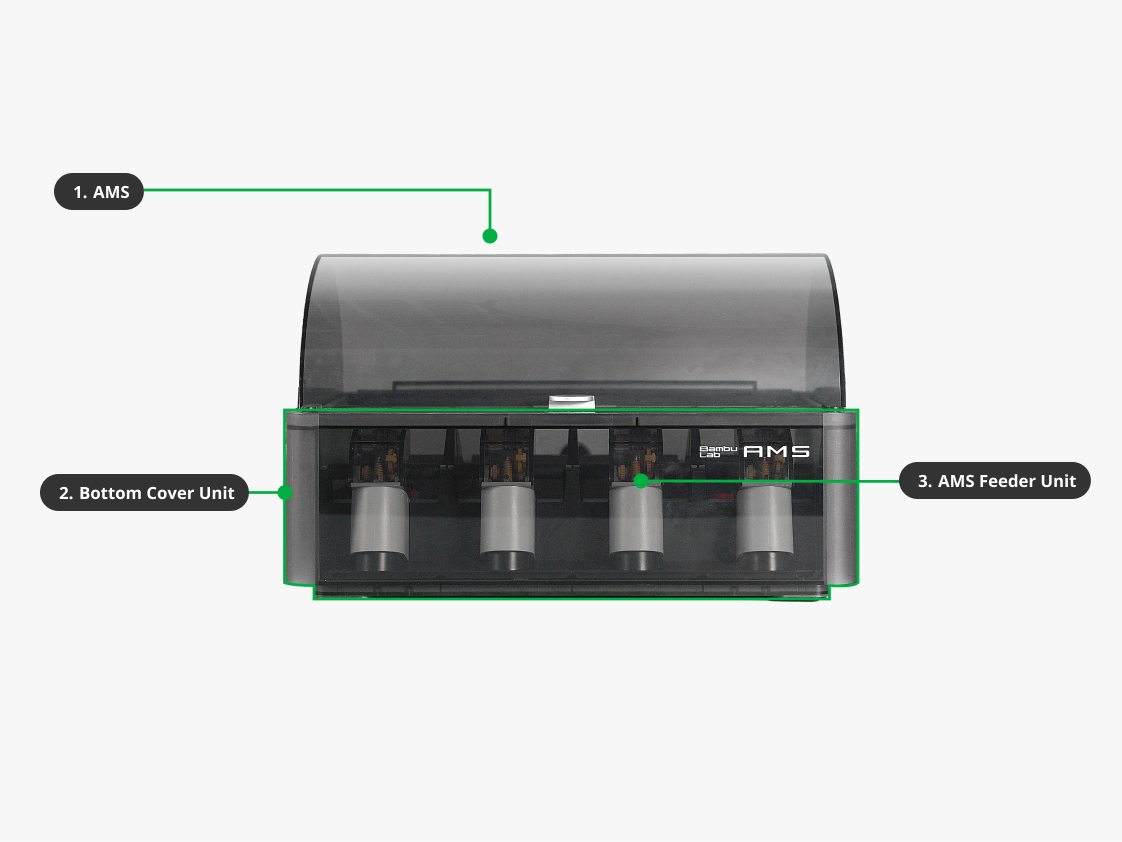
| 1. AMS | AMS, short for Automated Material System, collaborates with 3D printers to accomplish automated multi-color printing. AMS lite is one variant of the Automated Material Systems developed by Bambu Lab. |
| 2. Bottom Cover Unit | A bottom shell of the AMS with all sealings installed. |
| 3. AMS Feeder Unit | The AMS feeder unit is specially designed to support the AMS for printing multiple colors and materials. Each AMS has 4 feeder units, and each feeder unit has its own motor and gears to actively push the filament forward or wind it back to the spool. The feeder unit has a sensor to detect filament. When a filament is inserted, the feeder unit will pull the filament automatically. When the filament needs to be winded back, the feeder unit will drive the AMS driving sleeve to rotate the spool for filament winding. |
¶ Internal View
.png)
| 1. Filament Slot | Slots for the filament on the AMS ensures the smooth feed of the filament to the extruder. |
| 2. Driven Support Shaft Assembly | A roller for supporting the filament spool. |
| 3. Internal Hub Motor | It is used to provide energy for the operation of the AMS internal hub unit. |
| 4. Power Board | It is a circuit board that receives power from the printer and supplies it to the AMS. |
| 5. Active Extrusion Wheel Assembly | A gear assembly in the AMS filaments hub that directly drives the filament. |
| 6. Feeder Funnel Unit | It is the inner component of the AMS feeder unit, which consists of structural parts and a filament detection sensor board. When the sensor board detects the insertion of filament, the AMS feeder unit will pull the filament forward automatically. When the filament insertion is abnormal, the sensor board will also identify it and feed that information back to the 3D printer. |
| 7. Active Support Shaft Assembly | A roller for supporting the filament spool and also for actively driving the spool to roll. |
| 8. RFID Board | It can automatically identify the RFID tag on Bambu filament spools. The information is then synchronized to the Bambu Studio. |
| 9. Internal Hub Unit | It is located at the bottom of AMS. It consists of four filament sensors, one magnetic rotary encoder, and one brushless motor. It merges four filament paths into one. The filament sensor detects when the filament has reached a specific location, which in turn activates the brushless motor to give the filament a second stage driving force. |
¶ AMS lite
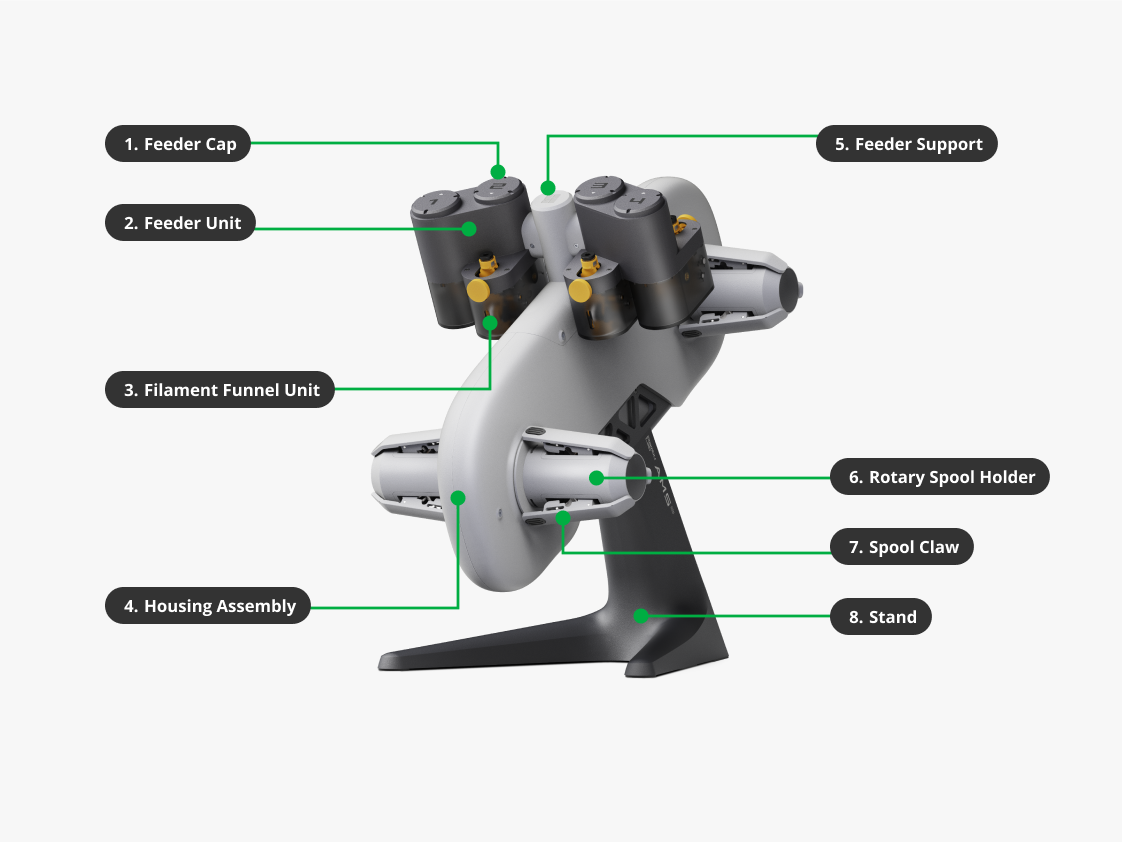
| 1. Feeder Cap | The top cover for the AMS lite Feeder Unit, and is marked with numbers. |
| 2. Feeder Unit | A plastic connector that connects the two AMS lite Feeder Units together, and fix them to the AMS lite body. |
| 3. Filament Funnel Unit | It is the inner component of the AMS lite feeder unit, which consists of structural parts and a filament detection sensor board. When the sensor board detects the insertion of filament, the AMS first stage feeder will pull the filament forward automatically. When the filament insertion is abnormal, the sensor board will also identify it and feed that information back to the 3D printer. |
| 4. Housing Assembly | It is the outer casing of the AMS lite body. It provides protection for the internal structure of the AMS Lite. |
| 5. Feeder Support | A plastic connector that connects the two AMS lite Feeder Units together, and fix them to the AMS lite body. |
| 6. Rotary Spool Holder | It is designed to support and hold the spool when it's attached to the AMS lite. Each rotary spool holder has 3 spool claws to secure the spool in place. While the feeder unit pulls the filament, the rotary spool holder works in coordination to enable the spool to rotate during the printing process. This ensures continuous filament feeding and smooth operation. |
| 7. Spool Claw | It is assembled on the rotary spool holder and is used to secure the spool in place. The 3 rubber pads on the claws are used to increase the friction between the claws and the spool, preventing the spool from detaching from the spool holder during the printing process. |
| 8. Stand | A bracket that support the AMS lite body. |
¶ Cutting module
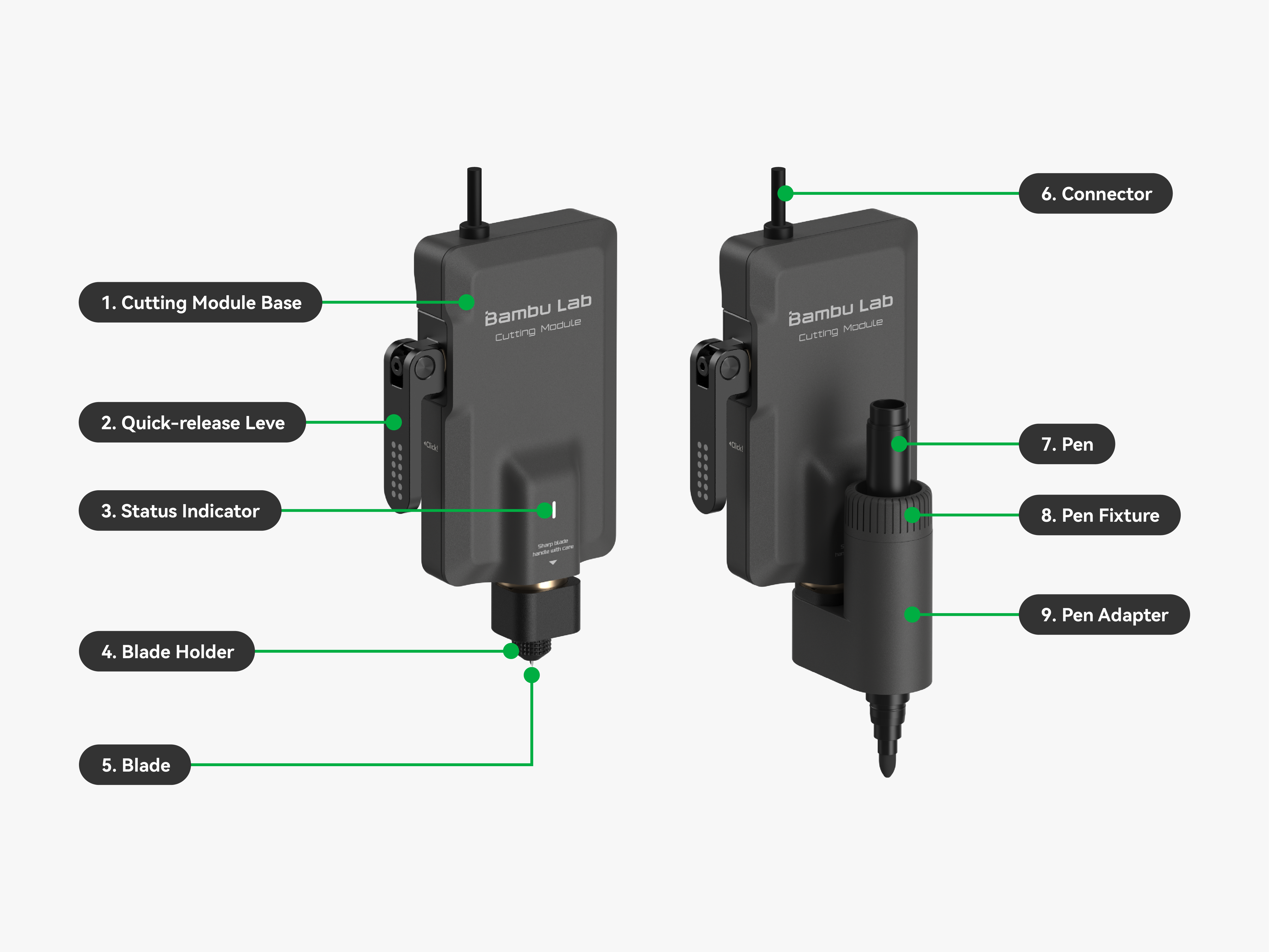
| 1. Cutting Module Base | It connects the blade holder to the module and secures it in place for stable installation. |
| 2. Quick-release Lever | It is a tool-free mechanical structure that allows for quick installation and removal of the cutting module. |
| 3. Status Indicator | It indicates the current operating status of the cutting module. |
| 4. Blade Holder | It secures the blade to ensure stable operation and easy replacement. |
| 5. Blade | It uses a 45° pointed blade for high-precision cutting. |
| 6. Connector | It connects the cutting module to the printer, responsible for supplying power and transmitting control signals to the module. |
| 7. Pen | A tool used for painting or writing. |
| 8. Pen Fixture | It secures the pen to ensure it remains stable during drawing. |
| 9. Pen Adapter | It connects the pen to the blade holder for easy replacement. |
¶ Laser module
Illustrated with the Bambu Lab Laser 10W.
¶ Front View
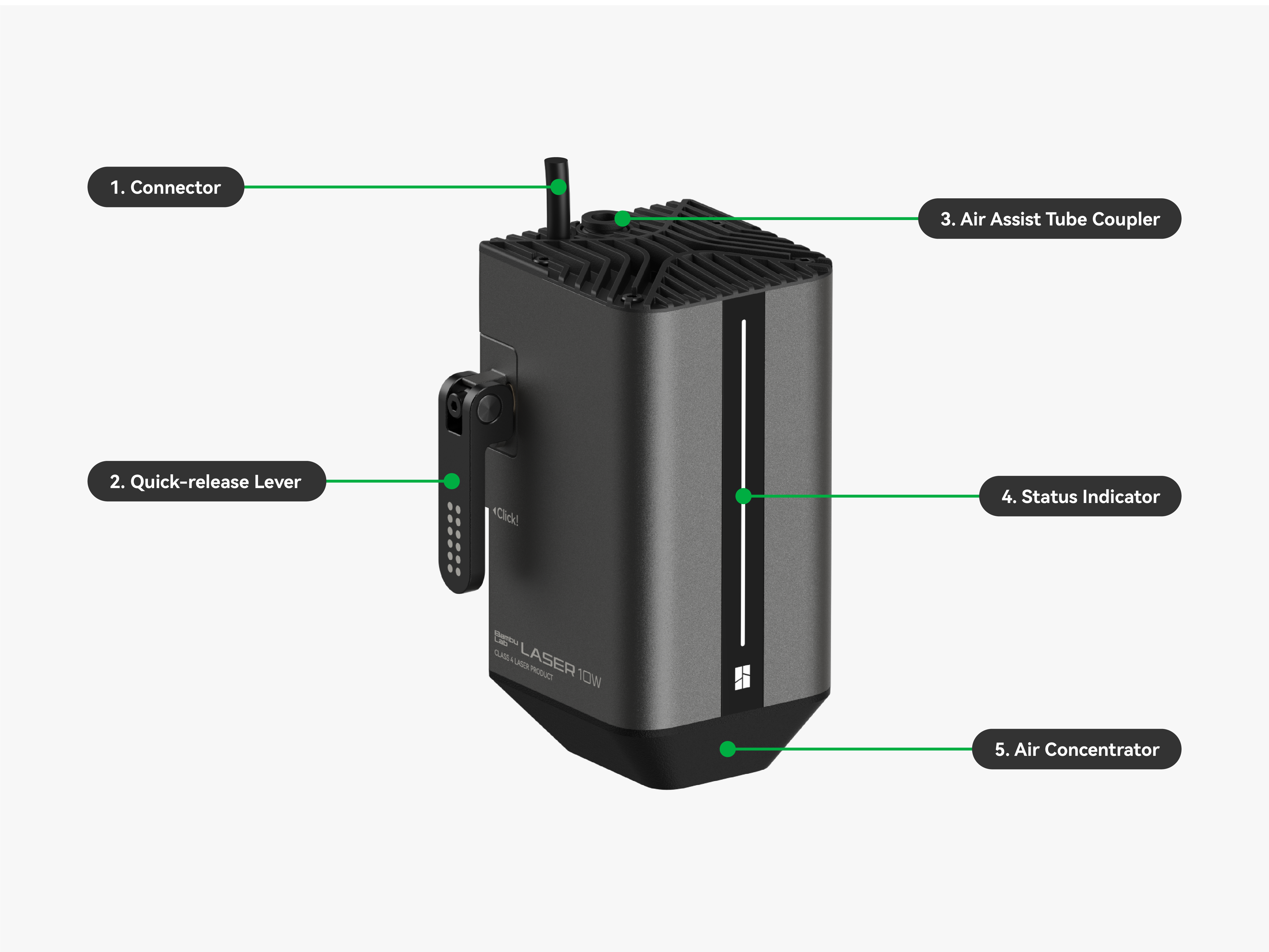
| 1. Connector | It connects the laser module to the printer, responsible for supplying power and transmitting control signals to the laser module. |
| 2. Quick-release Lever | It is a mechanical structure enabling tool-free and quick mounting and removal of the laser module. |
| 3. Air Assist Tube Coupler | It connects the air tube to the laser module, ensuring stable airflow delivery from the air pump. |
| 4. Status Indicator | It is an indicator that shows the current operating status of the laser module. |
| 5. Air Concentrator | It concentrates airflow to the laser processing area to reduce smoke, minimize heat buildup, and improve processing quality. |
¶ Bottom View
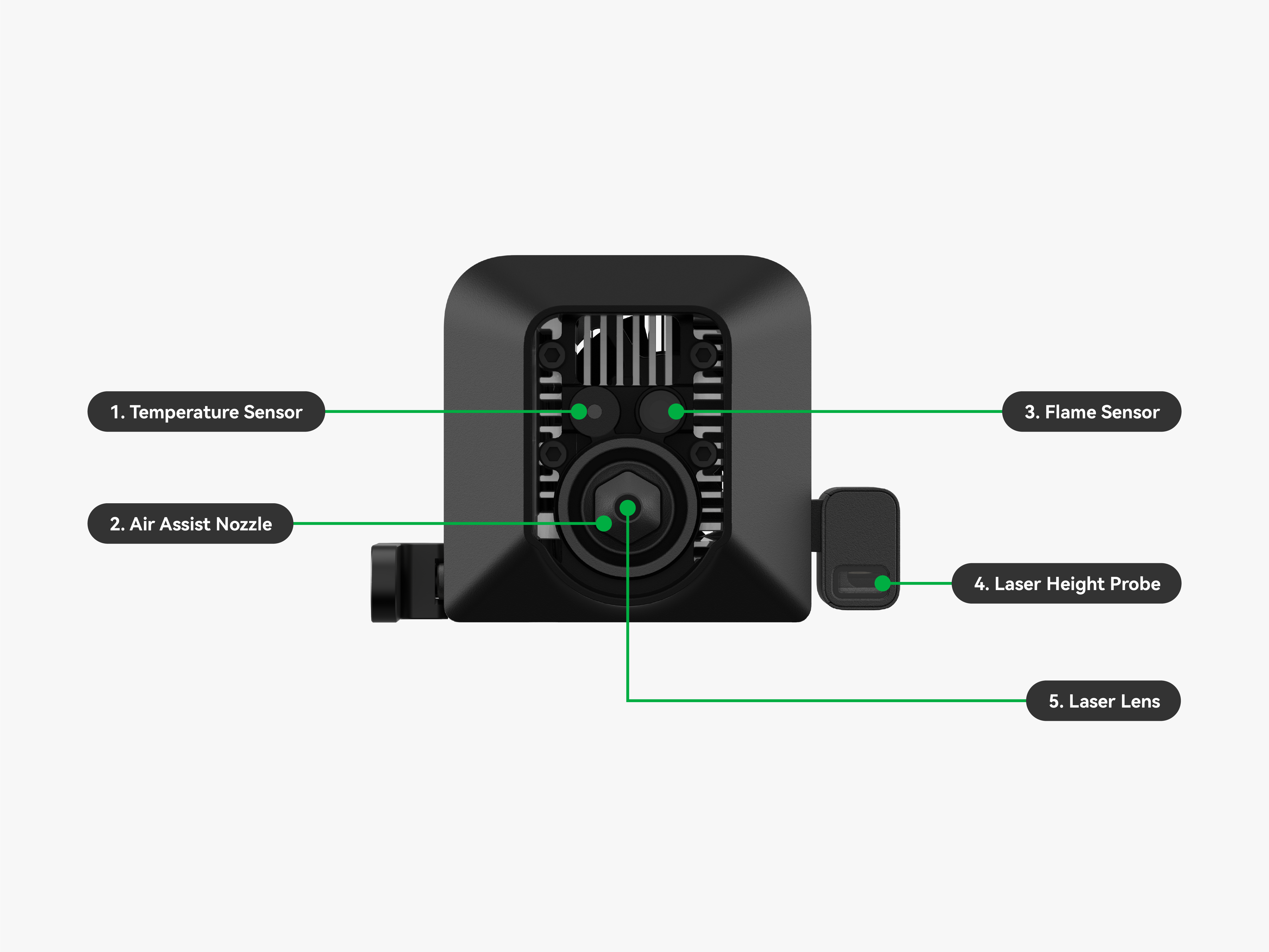
| 1. Temperature Sensor | It monitors the temperature of the laser module to prevent overheating that could cause damage or safety hazards. |
| 2. Air Assist Nozzle | It precisely directs high-pressure airflow toward the processing point to remove smoke and dust, improve cooling efficiency, and enhance the surface quality of the workpiece. |
| 3. Flame Sensor | It detects flames or flashes inside the device and promptly triggers an alarm to ensure processing safety. |
| 4. Laser Height Probe | It measures the distance between the material surface and the laser module using an infrared time-of-flight sensor to calculate material thickness to enable automatic focusing and precise processing. |
| 5. Laser Lens | It is used to collimate and focus the laser beam, minimizing divergence and improving transmission stability and processing precision. |
¶ Other Terms
¶ AMS
| AMS Feeder Unit | The AMS feeder unit is specially designed to support the AMS for printing multiple colors and materials. Each AMS has 4 feeder units, and each feeder unit has its own motor and gears to actively push the filament forward or wind it back to the spool. The feeder unit has a sensor to detect filament. When a filament is inserted, the feeder unit will pull the filament automatically. When the filament needs to be winded back, the feeder unit will drive the AMS driving sleeve to rotate the spool for filament winding. |
| AMS Mainboard | It is the center circuit board of the AMS. It provides a series of connectors through which the various functional components are connected by cables. |
| AMS Rubber Seal | It keeps the inside of the AMS dry, reducing the rate at which filaments and desiccants absorb water from the air. |
| Filament Buffer Connection Board | It is located inside the AMS filament buffer and is equipped with a Hall sensor. It can monitor the feeding status of the AMS by detecting the position change of the buffer slider. |
| Bambu Bus Cable - 4pin | It connects the printer to filament bub or buffer. |
| Bambu Bus Cable - 6pin | 1. Connects an AMS to another AMS which is located at a shorter distance 2. Connects an AMS to the AMS hub or filament buffer. |
| Bambu 4-in-1 PTFE Adapter | It is an adapter used to connect the PTFE tube. Compared to the original PTFE tube coupler, the 4-in-1 adapter can connect 4 feeder modules to the printer at the same time. Up to 7 different filaments: 1 AMS and other 3 filaments. It can help users to connect the printer to AMS along with other filaments which are not compatible with AMS such as TPU 95A, Bambu PET-CF and other brands' filaments that contained carbon fiber/glass fiber. |
| AMS Active Extrusion Wheel Assembly | A gear assembly in the AMS filaments hub that directly drives the filament. |
¶ AMS Lite
| AMS lite Feeder Motor | The motor installed inside the AMS lite Feeder Unit, and it is used to drive the feeder to send out the filament. |
| AMS lite 4-Pin Cable | It is used to connect the printer and the AMS Lite device. It serves two functions: providing power from the printer to the AMS Lite and facilitating communication between the two devices. This enables the printer to control the AMS Lite, allowing it to read information from the filament spool RFID tag and manage the switching/extrusion of multi-color 3D printing filaments. |
| AMS lite Filament Hub Unit | It is a key part of reliable filament switching during multi-color or multi-filament printing. One end of the unit connects to 4 different PTFE tubes (up to 4 filaments), while the other end connects to the top of the extruder to feed filament. |
| AMS lite Top Mount Screws Kit | It contains all the neccessary screws for installing the Top Mount Bracket Set on top of the Bambu Lab A1 printer. The screws kit can help to safely mount the AMS lite. |
| AMS lite Mainboard | It is a circuit board installed inside the AMS lite. After connecting to the printer, it can control AMS lite to complete the automatic material changing function. |
¶ Toolhead
| Toolhead Cable | It is the data transmission cable that connects the toolhead to the main board, responsible for transmitting control signals and supplying power to the toolhead. |
| Toolhead Front Carriage | It is the protective cover over the front of the toolhead block, shielding internal components from dust and damage. |
| TH Board Set | It includes the extruder board, Extruder Interface Board, and TH Board FPC Cable. They can be replaced according to the damaged parts. |
| TH Board FPC Cable | It is used to connect the TH control board to other components, ensuring the transmission of electrical signals. |
| Extruder Connection Board | It is the extruder connection board on the toolhead, used to connect the hotend and extruder related functional components. |
| Extruder Filament Sensor | It is installed on the extruder to detect whether the current printing filament has been delivered to the extruder and whether the cutter rod is released normally. |
| Extruder Motor | It is installed on the toolhead and used to drive the movement of the extruder. |
| Complete Bambu Hotend - Hardened Steel | It is a hotend assembly with a hardened steel nozzle. In addition to the nozzle, it also includes a ceramic heater, a thermistor, a cooling fan, and a silicone sock. Compared with stainless steel, hardened steel is not only suitable for common 1.75mm 3D printer filaments, but also for engineering filaments such as nylon carbon fiber and nylon glass fiber. It provides superb toughness and longevity, and is very simple to install and replace. |
| Complete Bambu Hotend - Stainless Steel | It is a hotend assembly with a hardened steel nozzle. In addition to the nozzle, it also includes a ceramic heater, a thermistor, a cooling fan, and a silicone sock. It is made from stainless steel to provide high-temperature resistance and corrosion resistance. |
| Hotend Heating Assembly | It is used to heat the nozzle to the required temperature. |
| Extruder Unit | It is responsible for pulling the filament out of the spool and feeding it into the hotend. The extruder needs to accurately control the length of the filament extruded through the hotend and is one of the core components of a 3D printer. |
| Extruder Unit Front Cover | It is an external protective component of the 3D printer's extruder, shielding internal parts from dust and external influences while also enhancing safety. |
| Filament Sensor Base | It is installed on the top of the extruder unit of the toolhead and is used as a fixed base for mounting the filament sensor on its side. It also serves as the base for the filament hub of A1 series printers. |
| Hardened Steel Extruder Gear Assembly | It is an internal gear component of the extruder unit. It comprises a driven gear and an active gear that work together to feed filament into the hotend. |
| Direct Drive Extruder | It is a design where the extruder is mounted directly on the toolhead, improving control and response speed for filament feeding. |
| Carburized steel drive gear | It is a part of the extruder, a gear made of hardened material to make it more durable and resistant to wear from hard materials. |
| Thermistor for Hotend | It has highly accurate temperature measurement and reliable structural design. It is for use with Bambu Lab complete hotend assembly only. |
| Ceramic Heater for Hotend | It can heat the nozzle up to 300℃, which is for use with Bambu Lab complete hotend assemby only. |
¶ Heatbed
| Heatbed Signal Cable | It is a 6 pin cable that connects the MC board to the heatbed. |
| Heatbed Piezo Interface Board | It is a small circuit board installed in the heatbed, connecting heatbed sensor 1 and heatbed sensor 2. There are 2 of them. |
| Heatbed Surface Magnet | It is a soft rubber plate with magnetic properties attached to the surface of the aluminum base plate of the heatbed. It is a component of the heatbed and its main function is to adsorb the build plate so that the build plate can be stably adsorbed on the heatbed. |
| Heatbed Unit | The main function of the heatbed is to heat the printing surface to help the printed layer adhere better to the build plate. If the printing surface is not heated, the first layer of filament deposited on the heatbed may not be able to stably adhere to the heatbed surface, causing the print to warp or even fall during subsequent printing. |
| Heatbed Sensor Unit | It is a piezoelectric ceramic with a bracket installed, and is used to detect the condition of the surface pressure on the heatbed. There are 3 sensors installed on the bottom of the heatbed. |
¶ Accessories
| Glue Stick for Build Plate | Provides suitable adhesion between the build plate and the model, and also it's formaldehyde-free. |
| Liquid Glue for Build Plate | The Bambu Lab liquid glue is an adhesive specially developed for 3D printing, suitable for printing materials such as PLA, ABS, and PETG on appropriate surfaces, including the Cool Plate, High-Temperature Plate, and Textured PEI Plate. When using Bambu Lab Liquid Glue, constant adhesion is maintained without worrying about models falling off or warping. |
| Lubricant Grease and Lubricant Oil | Lubricant Grease is used for lubricating lead screws or eliminating noise issues between belts and idler pulleys. Lubricant Oil is typically used for the lubrication of linear guides, slide rails, and steel shafts. |
| AB Glue | It is a two-component adhesive commonly used for bonding and repairing 3D printed models. |
| Unclogging Pin Tool | It is a tool for clearing clogged nozzles to ensure a smooth printing process. |
| Bambu Scraper | Use a sharp scraper for releasing the model from the printing surface can prolong the lifetime of the build plate. After the plate has cooled down, gently slide the scraper underneath one of the corners of the model then carefully bend the sheet to remove the model. |
| Desiccant for AMS (6 pack) | Place inside the AMS to keep the air inside dry, thus protecting the filaments from moisture. |
| Kafuter Reinforced Casters Glue | A high-performance adhesive with strong adhesion and durability, especially in environments that require high strength and temperatures resistance. |
| Cable Box | Used to fix the USB-C cable, Z motor cable, X motro cable, and the camera cable. |
| Activated Carbon Air Filter | It is a component used to filter harmful gases produced during printing, improving the printing environment. |
| Bambu Filament Swatches | A reference when you are looking for a type of filament with a certain color. Also, the 5-digit code can be used to quickly locate the filament in our store. |
| Hotends Kit | It includes 3 nozzles (0.2mm/0.4mm/0.6mm) and 3 hotend silicone socks. |
| Purge Wiper | It is designed to efficiently remove waste filament generated by the printer's hotend. It gathers and dislodges waste filament during different stages, including printer setup, pause and resume operations, and filament changes for multi-color printing. Its purpose is to ensure the proper management and disposal of waste materials for seamless printing processes. |
| Thermal Paste | It is used to improve the thermal conductivity of NTC, hotend and nozzles. |
| Cable Chain | With it assembled, the trajectory of the toolhead cable and PTFE tube can be safely confined to the horizontal plane during printing. It can also protect the toolhead cable and feeding tube from being damaged during repetitive bending as a result of motion. |
| Bambu Backlight Board | Used in CMYK lithophane printing. It provides an even light source, making the effect more visible and vivid. |
| Filament Buffer | It is located at the back of the printer, connecting the AMS and the toolhead extruder, and consists of a slider, a spring, and a Hall sensor. The Hall sensor detects the position of the slider, and the filament buffer feeds the signal back to the AMS and the printer, thereby controlling the feed speed of the AMS. |
¶ Electrical components
| AC Board | It converts alternating current (AC) into usable voltage for the printer. |
| AP Board | It is a circuit board that controls the printer and provides the required Wi-Fi connectivity and processing power for the printer. |
| Bambu USB-C Cable | Used for communication between the toolhead and the mainboard. |
| Internal Power Supply | It is an AC to DC power converter, with variable input of 100-240V and output of 24V. It supplies power to the entire printer except the heatbed. |
| LOGO LED Cable | X Series: Connect from the front housing of the toolhead to the TH board. P Series: Connect from the front housing of the toolhead to the extruder connection board. |
| Power Cable | It is the cable that connects the printer to the power supply, responsible for transmitting electricity to power the device. |
| Screen Connector Cable | It is used to connect the printer's screen to the main board, responsible for transmitting display signals. |
| AC Power Cable | It is the cable that connects the 3D printer to an alternating current power source, responsible for supplying electricity to the device. |
| MC to AP Cable | The X1 series has two cables, and the P1 series has one cable. The cable connects the AP board and MC board of the X1 series printers, supplying the power from MC to AP, and and data interaction between them. |
| Button Board with Chamber Temperature Sensor | It is a circuit board installed in the upper-right corner of the X1 printer to control the emergency stop button and the sleep (screen off) button. It also contains the chamber's temperature sensor. |
| Chamber Heater Control Board | It is used to control the chamber heater. |
| Mainboard | It is the core control unit of the printer, responsible for processing all printing commands and controlling the various components of the device. |
| MC Board | It is the control center for the printer's moving parts. |
| Heatsink for MC Board | It is a cooling device used to dissipate heat from the MC control board of the printer, helping to lower the temperature and improve performance and stability. |
¶ Fan
| Auxiliary Part Cooling Fan | It is a powerful 12W cooling fan installed on the left side of the chamber. It provides a better cooling condition for high-speed printing. |
| Chamber Temperature Regulator Fan | It is responsible for adjusting the temperature within the chamber. Whether the fan is turned on and its speed are determined by the chassis temperature detected by the sensor. |
| MC Board Fan | A cooling fan for the MC board. |
| Cooling Fan for Hotend | It is used to enhance the temperature conduction of the hotend hea sink and prevent heat from being conducted to other components such as the extruder. The cooling fan is a high-speed rotating part, so do not touch it while it is running. |
| Part Cooling Fan | It is used to ensure adequate cooling of the printed layers during the printing process. It helps in rapidly cooling the material as it is extruded, allowing each layer to solidify and maintain its shape before the next layer is deposited. |
| Power Cooling Fan | It is a fan in the printer used to cool the power supply unit, helping to maintain an appropriate operating temperature. |
| Mainboard Fan | It is used to cool the mainboard to prevent the mainboard from overheating and shutting down. It cannot be manually controlled, and the printer automatically adjusts the speed. |
¶ Build Plate
| Bambu Engineering Plate | It is made by applying a special thermosetting coating on spring steel. This makes the printing plate stronger than PC and PEI sheets. It's ideal for printing engineering materials. However, one drawback is that you need to be strict about using adhesive (Bambu glue stick or liquid glue is recommended). If you don't apply adhesive properly, the plate might not stick well, leading to printing issues. |
| Bambu High Temperature Plate | It consists of two parts: the High Temperature plate sheet and the Engineering Plate. You can print on both sides of the plate. The high-temperature sheet is made of PEI, featuring a smooth surface and a fine matte texture. It's attached to the engineering plate using 3M high-heat-resistant double-sided tape. Unlike the PC sheet used in the Cool Plate, PEI material offers better heat resistance and is less likely to deform under high temperatures. This makes it more compatible with various filaments. Except for the PLA filament, When printing with other filaments, it's highly recommended to use adhesive (Bambu glue stick or liquid glue is recommended) to ensure proper adhesion between the filaments and the build plate. This is crucial to prevent the risk of cracking the high-temperature sheet. |
| Bambu PLA Plate | It's a build plate specifically designed for printing with PLA filament, typically featuring good adhesion to ensure that the printed model does not detach during the printing process. |
| Bambu Dual Texture PEI Plate | One side is a textured PEI, which brings a grainy surface to models, and the other side is a smooth PEI, which brings a smooth surface to models. |
| Bambu Smooth PEI Plate | It is obtained by adhering a carefully selected PEI sheet to a spring steel using a highly heat-resistant 3M adhesive. The Smooth PEI Plate provides a flat surface for printed objects and is suitable for scenarios that require a level bottom surface. The PEI sheet on the surface of the Smooth PEI Plate allows for printing with various filaments. Only PLA filament does not require glue, while printing with other filaments requires the use of gluing to prevent the PEI sheet from tearing. The thicker 0.5 mm spring steel helps reduce the risk of warping in the printing plate. |
| Bambu Textured PEI Plate | It is made by coating a stainless steel sheet with a layer of PEI powder, creating a textured surface on both sides. What sets it apart is its special rough texture, which is transferred to the bottom surface of your prints. This plate works well with a variety of materials and often provides excellent adhesion without the need for adhesives, making it user-friendly. Additionally, the PEI coating on the plates is durable and has a long lifespan. |
| Galaxy Surface Plate | It is a build plate featuring a starry pattern, often used to enhance the adhesion of printed models while providing an aesthetically pleasing appearance. |
| Bambu Cool Plate | It consists of two parts: the Cool Plate sheet and the Engineering Plate. You can print on both sides of the plate. The cool plate sheet, made of PC, has a smooth surface. It's attached to the engineering plate using 3M high heat-resistant double-sided tape. This plate is specifically designed for printing PLA filament. However, if you try to print with materials like PETG or ABS, you might encounter issues like bubbling and sticking. It's important to remember that when printing PLA on the Cool Plate, you need to use a Bambu glue stick or liquid glue for proper adhesion. |
| Spare Sheet for Bambu Cool Plate | It is a spare sheet used with the Bambu cool plate, suitable for low-temperature filaments to enhance adhesion. |
| Spare Sheet for Bambu High Temperature Plate | It is a spare sheet used with the Bambu high temperature plate, designed for high-temperature filaments to ensure print quality. |
| Galaxy Surface Sheet | It is a surface sheet used for decorating the surface of 3D printed models, featuring a starry pattern that can be transferred onto the model. |
| Starry Surface Sheet | It is a surface sheet featuring an octagonal star pattern, used for decorating printed models. |
| Carbon Fiber Surface Sheet | It is a surface sheet that mimics the appearance of carbon fiber, used to give printed models a carbon fiber effect. |
| Diamond Surface Sheet | It is a surface sheet featuring a diamond pattern, used to decorate 3D printed models and enhance their visual appeal. |
| 3D Effect Sheet Combo | It is attached to the print plate, the pattern can be transferred to the 3D printed part. |
¶ Filament
| Bambu Reusable Spool | It is a spool for storing low-temperature filament (such as PLA or PETG), designed to maintain the filament's properties and quality at lower temperatures. |
| Bambu Reusable Spool (High Temperature) | It is a spool for storing high-temperature filament (such as PLA or PETG), designed to maintain the filament's properties and quality at elevated temperatures. |
| Bambu PLA Basic | A basic PLA filament, suitable for beginners and more advanced printing needs. |
| Bambu PLA Matte | A PLA filament with a more matte surface when printed, suitable for beginners and more advanced printing needs. |
| Bambu ABS | ABS filament for 3D printing; this is a somewhat more advanced filament but also a more robust material when printed. |
| Bambu TPU 95A | TPU filament for 3D printing more flexible items. |
| Bambu Support for PLA | A filament for printing support interfaces when printing with PLA; It is easy to remove once printing is complete. |
| Bambu Support for PA/PET | A filament for printing support interfaces when printing with PA or PETG; It is easy to remove once printing is complete. |
| Bambu PC | PC (Polycarbonate) filament, an engineering filament for advanced printing. |
¶ Printer Body
| Screen Rear Housing with Hinge | It is the back cover for the screen on a X1 series printer. It allows the screen to rotate up and down. |
| Glass Cover Plate | The P1 series and X1C use the same specification of glass cover plate that is installed on the top of the printer. It is used to support the AMS and enclose the printer to reduce heat loss. |
| Rear Bottom Cover | It is a protective component at the back of the printer, typically used to shield internal electronic components and provide structural support. |
| Front Cover | A black-gray cover that is installed on the front of the P1S printer, above the glass door. |
| Front Glass Door | It is to keep the inside of the printer closed, thus providing protection for the printing process while also insulating the enclosure for high-temperature printing. |
| Enclosed Chamber | The interior of the printer is covered with panels to form an enclosed printing chamber. |
| All-Metal Frame | It is the structural framework of the printer made from metal materials, providing greater stability and durability. |
| Polycarbonate enclosure | It is the printer casing made from polycarbonate material, providing good protection and thermal insulation. |
| Rear Bottom Cover | It is a protective component at the back of the printer, typically used to shield internal electronic components and provide structural support. |
¶ Mechanical Structure
| X-Axis Assembly | It ensures that the X-axis movement of the toolhead remains consistently fixed on the horizontal plane. The X-axis utilizes linear rail guidance, which provides stability, smooth motion, improved guiding precision, and longevity. |
| XY Belt | It is an open drive belt with a pitch length of 1442mm for X1 and P1 series printers. Its main function is to transmit the motion of the motor to the tool head with high precision. |
| XY Belt Tensioner with Pulley | It is composed of an idler pulley and a bracket, which can change the belt travel distance under the tension of the spring. |
| Y-Axis Assembly | It is responsible for controlling the movement of the heatbed on the Y-axis. |
| Y-Axis Tensioner | A component for tensioning the Y-axis belt of the A1 mini. |
| Y-Axis Top Cover | It is the protective cover over the top of the Y-axis assembly, preventing dust and debris from entering. |
| Heatbed Track Bearing | It supports the smooth movement of the Y-axis block, ensuring stability during the printing process. |
| Z Belt Timing Pulley | It is the pulley that drives the Z-axis movement, ensuring precise vertical movement of the heatbed. |
| Z-Axis Assembly | It is responsible for controlling the movement of the heatbed on the Z-axis. |
| Z-Axis Coupler | It is used to connect the Z-axis motor and the Z-axis lead screw. It enables precise transmission of motion and torque while accommodating certain levels of radial, axial, and angular misalignment. |
| Z-Axis Tensioner | It is used to adjust the tension of the Z-axis belt, ensuring stability and accuracy in the drive mechanism. |
| Z-Axis Top Cover | It is designed to protect the top of the Z-axis assembly. |
| Core XY Structure | It is a 3D printer motion control system, whose structure is based on the principle of two independent belts and two translation axes arranged in a staggered manner. |
| Full-Carbon X-rail | It is an X-axis guide rail made from all-carbon material, providing lighter weight and higher strength to enhance printing precision. |
¶ Chip and Algorithm
| Motion Control Algorithm | It is a mathematical model and program used to control mechanical movement to ensure precise positioning and movement. |
| Quad-core SOC | It is a system-on-chip that integrates four processing cores, capable of efficiently handling data and commands during the printing process. |
| Dual-Core MCU | It is a microcontroller with two processing cores, providing enhanced computing power to support the functions of the printer. |
| Dual-ABL with Dissimilar redundancy | Bambu Lab X1 utilizes two sets of independent sensors and an algorithm to measure the height of the nozzle relative to the bed. The lidar and analog force sensors crosscheck for an extra layer of redundancy in bed leveling. |
| RFID | It is a technology that uses radio waves for identification and tracking, which can be used for managing filaments and devices. |
| Cloud service | Provides data storage and management capabilities that enable users to manage print tasks from a cloud server. |
| Health management system (HMS) | HMS (Health Management System) is a function set up to facilitate the users of the Bambu Lab printer and AMS to troubleshoot the issues. The users can take advantage of notifications from HMS to know the system's status, including some mechanical and hardware errors, or the reason for printing failures. |
| Bambu Micro Lidar | It is a sensor capable of measuring depth in micrometers. Using this unit, the system can measure the distance, calibrate the flow extruded from the nozzle, and scan the first layer. |
| Door Sensor | The X1 Series intelligent door sensor automatically pauses printing when a door is opened, ensuring the safety of users of all ages. |
| Dual-ABL with Dissimilar redundancy | Bambu Lab X1 utilizes two sets of independent sensors and an algorithm to measure the height of the nozzle relative to the heatbed. The lidar and analog force sensors crosscheck for an extra layer of redundancy in bed leveling. |
¶ Bambu Studio / Bambu Handy
| Bambu Studio | It is a cutting-edge, feature-rich slicing software. It contains project-based workflows, systematically optimized slicing algorithms, and an easy-to-use graphical interface, bringing users an incredibly smooth printing experience. |
| Bambu Handy | An all-in-one mobile app designed specifically for Bambu 3D printers to remotely monitor and manage Bambu 3D printers, quickly and remotely initiate print tasks, or make adjustments to the print during the printing process. |
| Remote Printing | It is a feature that allows users to control and monitor the printing process remotely via the Internet. |
| Bridging | Bridge means the line that is completely extruded in the air, it is not supported by the last layer or heatbed, and the overhang degree reaches 100%. |
| Thick bridges | It refers to the extrusion of a bridge line that is equal in diameter to the nozzle. For example, using a 0.4mm nozzle to extrude a 0.4mm diameter bridge, the bridge line is called the thick bridge. |
| Top surface flow ratio | For the top surface, the actual flow ratio is calculated by multiplying the original flow ratio by this factor. This factor affects the amount of filament used for the top solid infill. |
| Initial layer flow ratio | The actual flow ratio is calculated by multiplying the original flow ratio by this factor. |
| Only one wall on top surfaces | With this option enabled, top surfaces will have only one wall, giving better appearance to top surfaces, especially for models with a flat top. |
| Top area threshold | This parameter can be configured after only one wall on top surfaces is enabled. This parameter affects the area threshold for the area of the wall that forms a single layer of the top surface. If part of the top surface is covered by a higher layer, such as the top of a sphere, then that top surface will not be considered as a top surface if its width is less than this threshold. |
| Smooth speed discontinuity area | Overhanging and non-overhanging areas usually have large speed variations, so enabling this option can make speed transitions smoother to improve cooling. |
| Smooth coefficient | It is used to control the length of the smooth transition path. The smaller the value, the longer the area of the speed transition, which means that the speed transition is smoother. Appropriate adjustment of the smoothing coefficient can make the print quality of the overhang area better, and it is usually recommended to set in the range of 1 to 100. |
| G-code | A command set used to control 3D printers, such as temperature and motions. |
| Slicing | A process that convers 3D models into g-code that 3D printers can understand. |
| Absolute Coordinates | This refers to a coordinate system that specifies positions based on a fixed origin point of the model. |
| Relative Coordinates | This refers to a coordinate system that describes positions based on the current location. Positions are specified in relation to the toolhead's last known position rather than a fixed origin. |
| Step Loss | It refers to a position shift detected by the motor. |
| First Layer | It refers to the first layer of the model that touches the heatbed. The quality of the first layer is crucial for 3D printers. If the first layer is not properly laid, it can lead to overall printing failures for the entire model. |
| Line Type | Different line types are displayed in various colors, showing information such as printing time, filament length, and weight required for each type. |
| Layer Height | The thickness of each layer printed, which typically affects the vertical resolution of the model. |
| Line Width | The width of the filament extruded by the nozzle. |
| Layer Time | The printing time for each layer. Generally, a larger layer area requires a longer printing time. |
| Infill Direction | The angle and overall direction of the infill pattern. |
| Minimum Sparse Infill Threshold | Areas of sparse infill smaller than this threshold will be replaced with solid infill. |
| Infill Combination | Automatically Combine sparse infill of several layers to print together to reduce printing time. |
¶ Print Quality
| String | Fine filaments that appear between printed parts during 3D model printing, usually caused by leakage during traveling. |
| Ringing | It is a visual artifact that typically occurs around the sharp corners or edges of a 3D printed object, appearing wavy or rippled. |
| Clogging | It refers to the situation where the nozzle or the extruder of the 3D printer becomes clogged by filament, preventing proper extrusion or feeding. |
| Warping | When the corners of the printed object detach from the printing platform during the printing process, it can cause deformation or warping of its bottom. |
| Oozing | Oozing refers to the phenomenon that the printer nozzle accidentally leaks out the melted filament before printing the model. |
| Shrinkage | It refers to the reduction in size or volume of a 3D printed object as it cools down. |
| Spaghetti | This refers to when the printing fails, the filament extruded from the nozzle appears on the build plate like a ball of spaghetti, usually caused by poor bonding of the printed object. |
| Wear | It refers to the gradual degradation or damage of printer components or parts due to friction, abrasion, or stress. |
| Layer lines | It refer to the visible lines or ridges on the surface of a printed object caused by the layer-by-layer manufacturing process in 3D printing. |
| Under-extrusion | It occurs when the printer extruder fails to extrude enough material, resulting in gaps or missing layers on the surface of the printed object. |
| Over-extrusion | It happens when the printer's extruder pushes out too much filament, leading to excess material and poor print quality. |
| Pillowing | It occurs when the top layers of a printed object are not tight enough, resulting in visible gaps or indentations on the surface. |
| Z-banding Z | It refers to visible horizontal lines or stripes on the surface of a printed object caused by inconsistent layer height or mechanical issues with the printer's Z-axis. |
| Seam | It refers to the starting and ending points of the extruder as it prints each layer of the object. |
| Elephant Foot | In FDM 3D printing, the material is extruded layer by layer through the nozzle to construct the 3D model. So during the printing, the first layer of extruded filaments is pressed onto the heat bed and has not yet fully cooled. In addition, the compression from the upper layer of gravity may cause the printed first layer to expand, which is called elephant foot. |